HSBC Real Economy Green Investment Opportunity Global Emerging Market (REGIO)
Enabling investors to align their financial objectives with real economy impact to deliver against the Paris Climate Agreement and Sustainable Development Goal agenda. A unique investment solution that combines both public and private sector capital to invest in a diverse range of Emerging Market (EM) green bonds outside the financial sector (the real economy).
Investment Objective
The UN-sponsored Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Paris Climate Agreement set a long-term transformational framework for the global economy with meaningful investor consequences if they fail to deliver.
Emerging markets have an urgent need to attract investment to tackle climate-change mitigation and adaptation to meet these goals. However, these markets are more likely to suffer the cost of climate change whilst being less able to self-finance solutions. This means that investors are exposed directly and indirectly to climate and sustainability risks across the financial system and in emerging markets in particular.
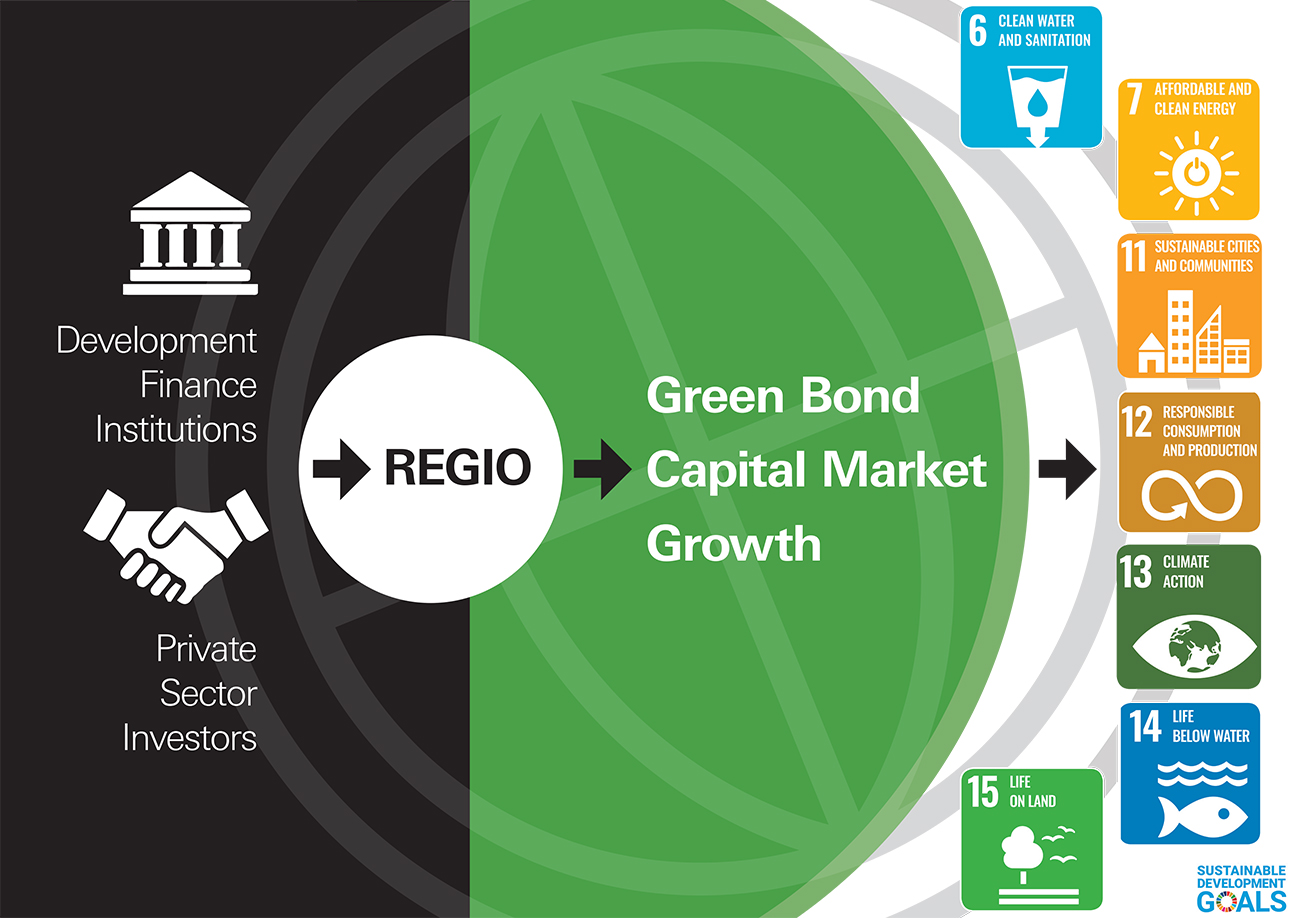
Investment opportunity
HSBC Asset Management, together with leading Development Finance Institutions (DFIs), have created an innovative investment solution to these challenges. REGIO will seek to:
- Invest in a diversified portfolio primarily comprised of emerging market green bonds and other similar bonds, principally issued by corporate issuers, on a buy-and- maintain basis
- Deliver real economy impact in primarily lower Gross National Income (GNI) countries
- Enable investors to achieve long-term, sustainable returns, whilst delivering on broader climate and environmental objectives in line with the SDGs and Paris Climate Agreement
HSBC Asset Management strengths
Emerging markets are part of our corporate DNA and we have one of the longest track records in the EMD universe, dating back to 1998.
- A global investment platform allows us to leverage the insights and local knowledge of our on-the-ground network of analysts and investment professionals from across the world
- EMD capabilities range from US dollar-denominated sovereign, quasi-sovereign and corporate bonds to local currency-denominated debt and local FX. We offer both benchmarked and total return strategies in this space
For more information or to discuss your investment strategy, contact us.
Risks in consideration
There is no assurance that a portfolio will achieve its investment objective or will work under all market conditions. The value of investments may go down as well as up and you may not get back the amount originally invested. Portfolios may be subject to certain additional risks, which should be considered carefully along with their investment objectives and fees.
- Fixed income is subject to credit and interest rate risk. Credit risk refers to the ability of an issuer to make timely payments of interest and principal. Interest rate risk refers to fluctuations in the value of a fixed income security that result from changes in the general level of interest rates. In a declining interest rate environment, a portfolio may generate less income. In a rising interest-rate environment, bond prices fall
- High Yield Investments in high yield securities (commonly referred to as “junk bonds”) are often considered speculative investments and have significantly higher credit risk than investment grade securities. The prices of high yield securities, which may be less liquid than higher rated securities, may be more volatile and more vulnerable to adverse market, economic or political conditions
- Foreign and emerging markets Investments in foreign markets involve risks such as currency rate fluctuations, potential differences in accounting and taxation policies, as well as possible political, economic, and market risks. These risks are heightened for investments in emerging markets which are also subject to greater illiquidity and volatility than developed foreign markets
- Derivative instruments Derivatives can be illiquid, may disproportionately increase losses and may have a potentially large negative impact on performance
Find out more about Responsible investing
Document
HSBC Real Economy Green Investment Opportunity GEM Bond Fund - Trial Balance Report Q3 2022
HSBC Real Economy Green Investment Opportunity GEM Bond Fund - Trial Balance Report Q2 2022
HSBC Real Economy Green Investment Opportunity GEM Bond Fund - Trial Balance Report Q1 2022
HSBC Real Economy Green Investment Opportunity GEM Bond Fund - Trial Balance Report Q4 2021
HSBC Real Economy Green Investment Opportunity GEM Bond Fund - Trial Balance Report Q3 2021
HSBC Real Economy Green Investment Opportunity GEM Bond Fund - Trial Balance Report Q2 2021
HSBC Real Economy Green Investment Opportunity GEM Bond Fund - Trial Balance Report Q1 2021
HSBC Real Economy Green Investment Opportunity GEM Bond Fund - Trial Balance Report Q4 2020
What are the risks?
There is no assurance that a portfolio will achieve its investment objective or will work under all market conditions. The value of investments may go down as well as up and you may not get back the amount originally invested. Portfolios may be subject to certain additional risks, which should be considered carefully along with their investment objectives and fees.
- Exchange Rate Risk Changes in currency exchange rates could reduce or increase investment gains or investment losses, in some cases significantly
- Counterparty Risk The possibility that the counterparty to a transaction may be unwilling or unable to meet its obligations
- Liquidity Risk is the risk that a Fund may encounter difficulties meeting its obligations in respect of financial liabilities that are settled by delivering cash or other financial assets, thereby compromising existing or remaining investors
- Operational Risk may subject the Fund to errors affecting transactions, valuation, accounting, and financial reporting, among other things
- Derivatives Risk Derivatives can behave unexpectedly. The pricing and volatility of many derivatives may diverge from strictly reflecting the pricing or volatility of their underlying reference(s), instrument or asset
- Emerging Markets Risk Emerging markets are less established, and often more volatile, than developed markets and involve higher risks, particularly market, liquidity and currency risks
- Interest Rate Risk When interest rates rise, bond values generally fall. This risk is generally greater the longer the maturity of a bond investment and the higher its credit quality
- Default Risk The issuers of certain bonds could become unwilling or unable to make payments on their bonds
- Credit Risk A bond or money market security could lose value if the issuer’s financial health deteriorates
- Green Bond Risk Investment in green bonds involves additional risks compared to other bonds, including that: (i) the market for green bonds is smaller and less liquid than markets for other types of bonds; (ii) projects for which the proceeds of green bonds are used are not always precisely defined; and (iii) green bonds may produce a lower yield than other types of bonds

